-

Clean room classification In Pharmaceutical Industry Guidelines
Clean Room Classification in pharmaceutical Industry how it is done?. What is a clean room and clean room Classification in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing? Which are the different requirements of clean room class in pharmaceutical manufacturing ? Relation of Particle count and Viable Count requirements of different grades of Clean Rooms. Clean rooms in pharmaceutical industry are…
-
Gene-Editing Treatment for HIV-Virus
Novel CRISPR Gene-Editing Treatment for HIV- Virus. In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have successfully developed and tested a revolutionary gene-editing treatment capable of eliminating a virus related to HIV from the genomes of non-human primates. The study, published in the journal Gene Therapy, introduces a…
-
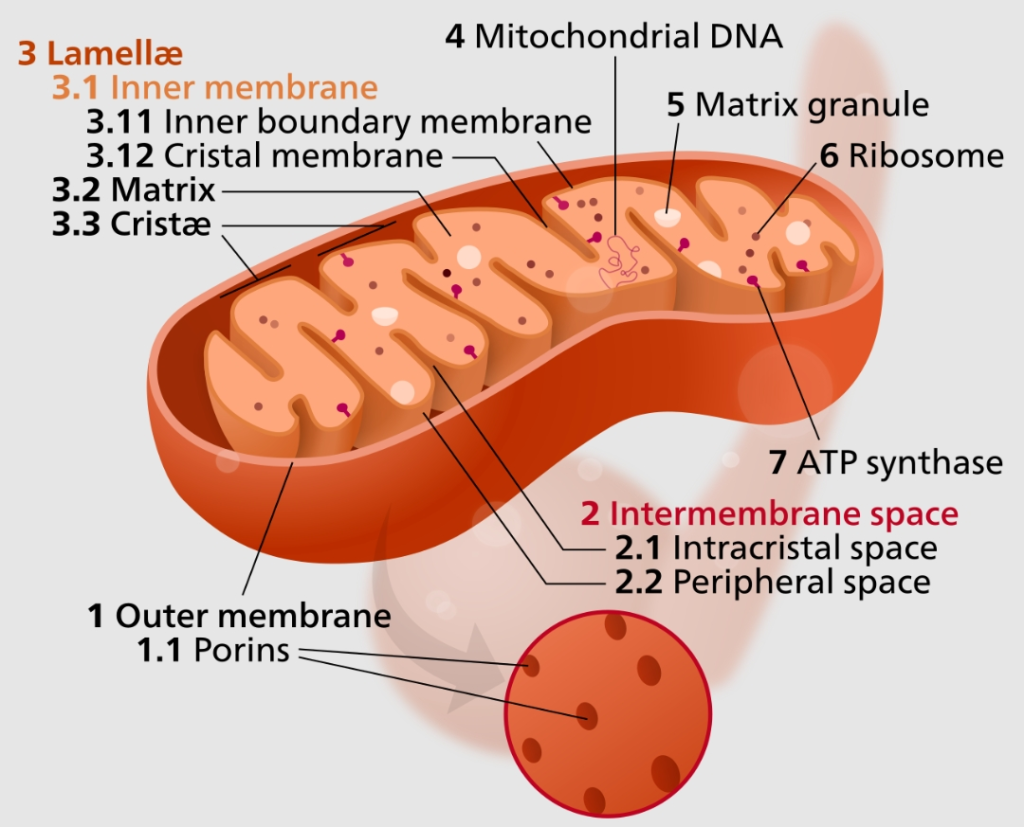
Mitochondrial Disease Causes Treatment
Detailed information on Mitochondrial disease it’s causes and treatment medicines used to treat their mode of action and side effects Mitochondrial Disease: Causes, Treatment, Medicines, and Their Mode of Action Mitochondrial disease is a complex and often debilitating group of disorders that affect the function of mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells. These disorders can…
-
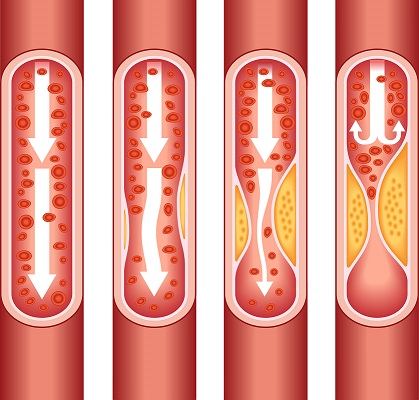
Coronary Arterial Calcium Scan Score Test
Coronary Calcium Scan Score Test: Unveiling Heart Disease Risk with Precision. Heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality globally, underscoring the significance of advanced diagnostic tools in assessing and mitigating cardiovascular diseases risks. Among these tools, the Coronary Arterial Calcium Scan Score Test has emerged as a valuable means to provide crucial insights into…
-
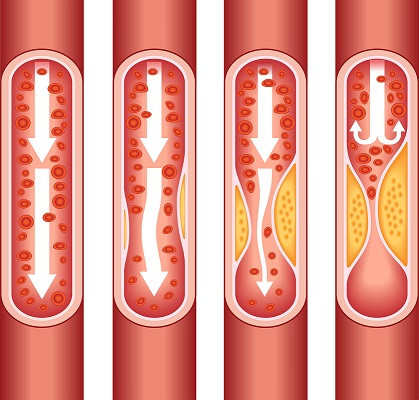
Preventing Heart Blockages
Proactive Steps to Safeguard Your Heart, prevent heart blockages. How to prevent Heart blockages? also known as coronary artery disease, pose a significant health risk and can lead to serious complications like heart attacks and strokes. Adopting a proactive approach to heart health is crucial in preventing the development of heart blockages. In this article,…
-

Pharmacology
Pharmacology: A Comprehensive Overview. Pharmacology is a pivotal discipline within the field of medicine that focuses on the study of how drugs interact with living organisms to produce therapeutic effects. It encompasses a wide range of topics and concepts that are fundamental to understanding the effects, mechanisms, and applications of drugs in healthcare. Here we…
-
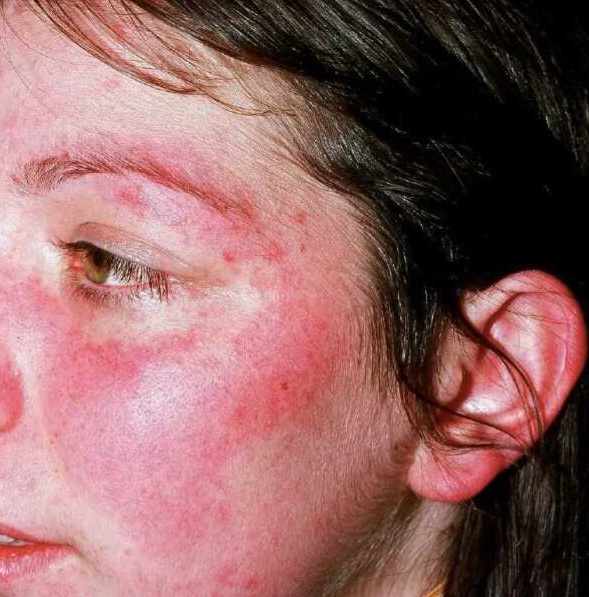
Allergies Causes Treatments and Medicines
Allergies Causes Treatments and Medicines mode of action of anti allergic drugs. Allergies are a common health concern affecting millions of people worldwide, let’s understand and discuss in detail information about allergies Causes Treatments and Medicines mode of action of Anti allergic medicines. Allergy occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to a substance it…
-
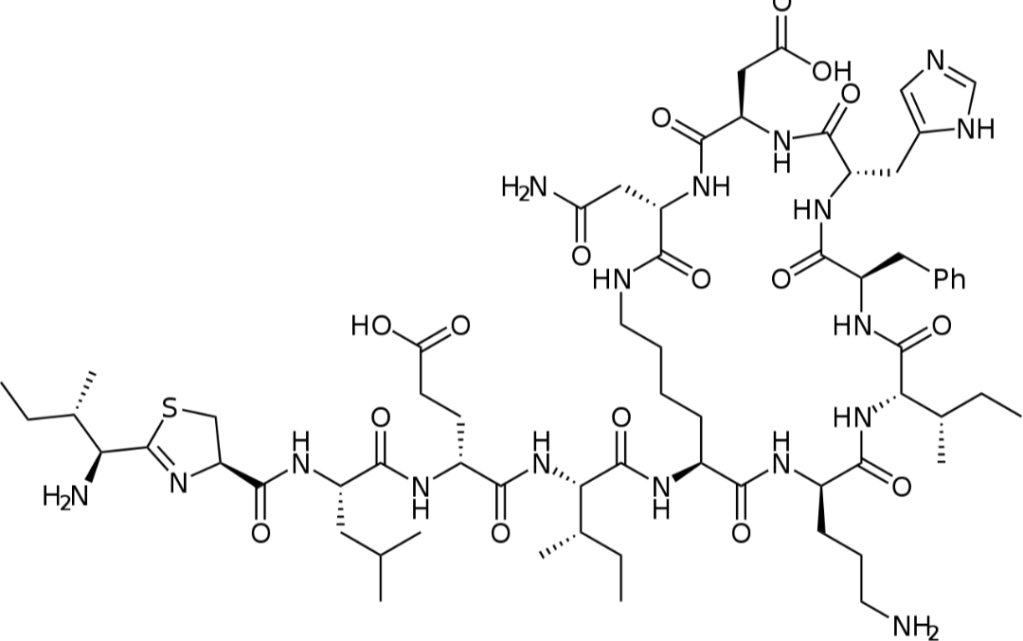
Bacitracin mode of action Side Effects Contraindications
Detailed information Bacitracin molecular structure mode of action drug interactions and contraindications. Bacitracin: Molecular Structure, Mode of Action, Drug Interactions, and Contraindications. Bacitracin, a widely used antibiotic, is a crucial component of modern medicine’s arsenal against bacterial infections. It is valued for its effectiveness and versatility in treating various types of skin infections, wounds, and…
-
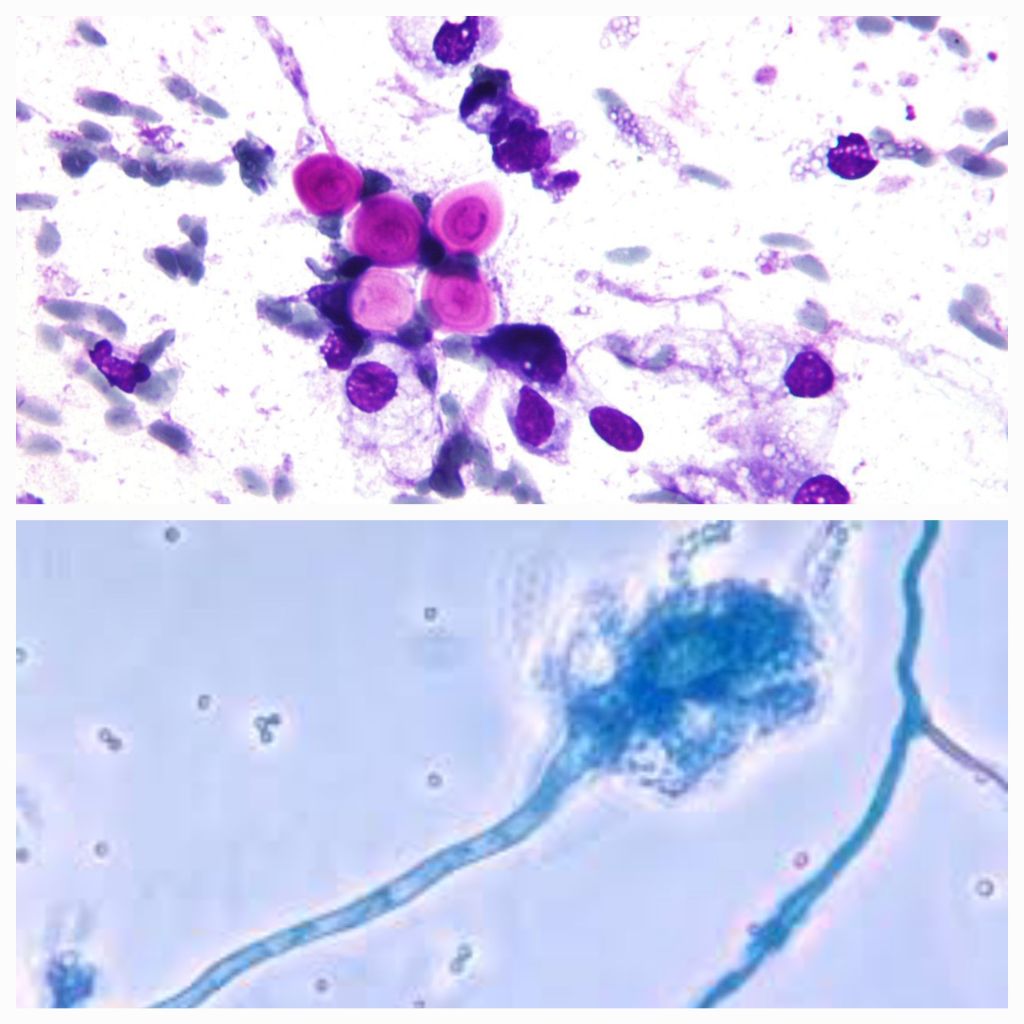
Sleep effects on Gut Microbes and Mental Health
The Vital Connection Between Sleep, Gut Microbes, and Mental Health. Do Sleep effects on Gut Microbes and Mental Health ? Sleep is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, essential for overall health and well-being. Recent research has shed light on the profound impact of sleep patterns on gut bacteria and how this, in turn,…
-
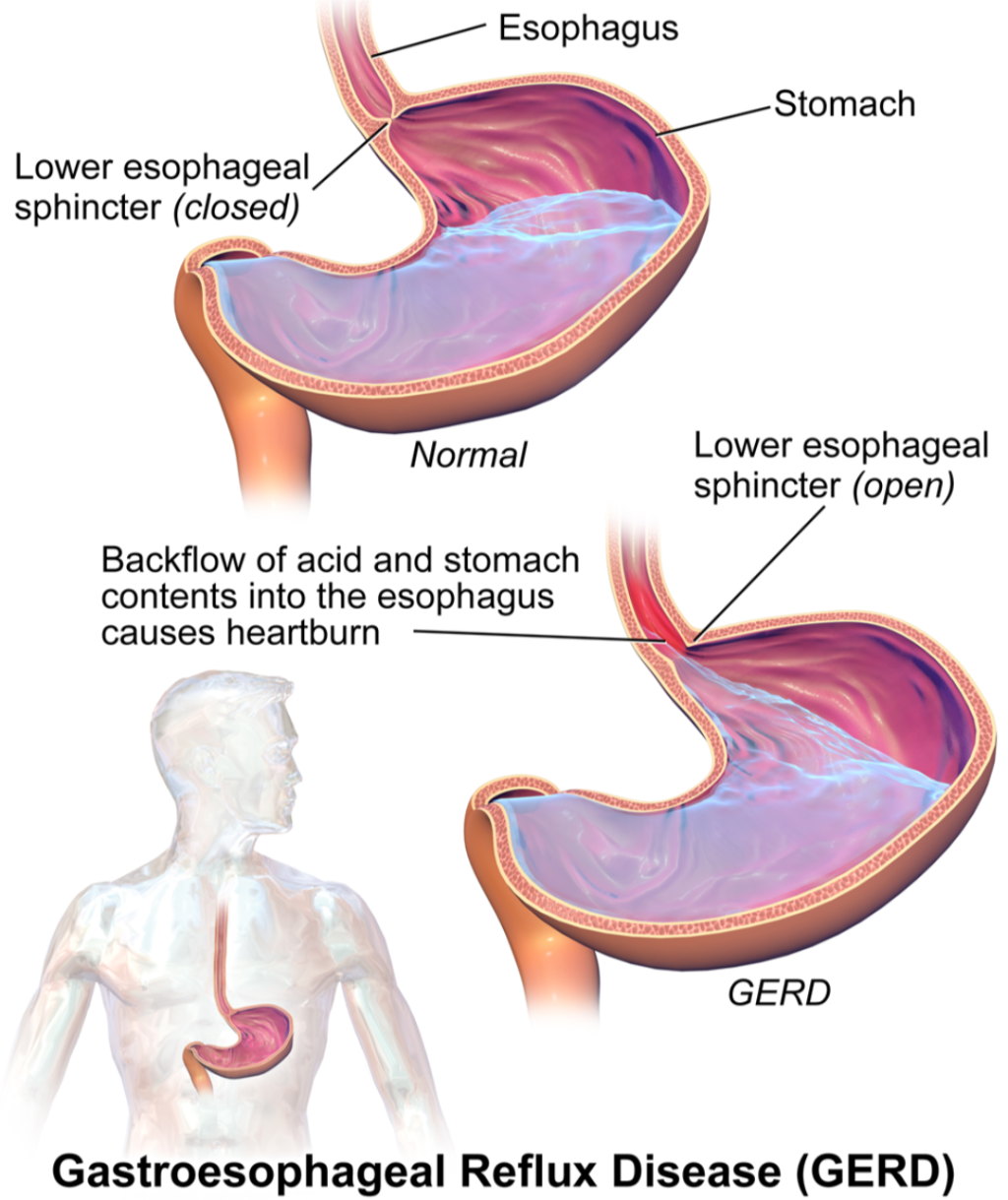
Acidity Causes Treatment Antacid Medicines
Detailed information about Acidity Causes and treatment with medicine in detail about antacid medicines their mode of action their daily dosage and side effects and Contraindications Understanding Acidity: Causes, Treatment, and Antacid Medicines Acidity, commonly known as acid reflux or heartburn, is a digestive disorder characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat.…
-

Antacid medicines dosage side effects Contraindications
Detailed information about the mode of action, dosage, side effects, and contraindications for drugs belonging to the classes of antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors: Antacids: Mode of Action: Antacids work by neutralizing excess stomach acid, thereby providing rapid relief from symptoms of acidity. They raise the pH of the stomach, reducing the acidity…