Detailed information about the mode of action, dosage, side effects, and contraindications for drugs belonging to the classes of antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors:
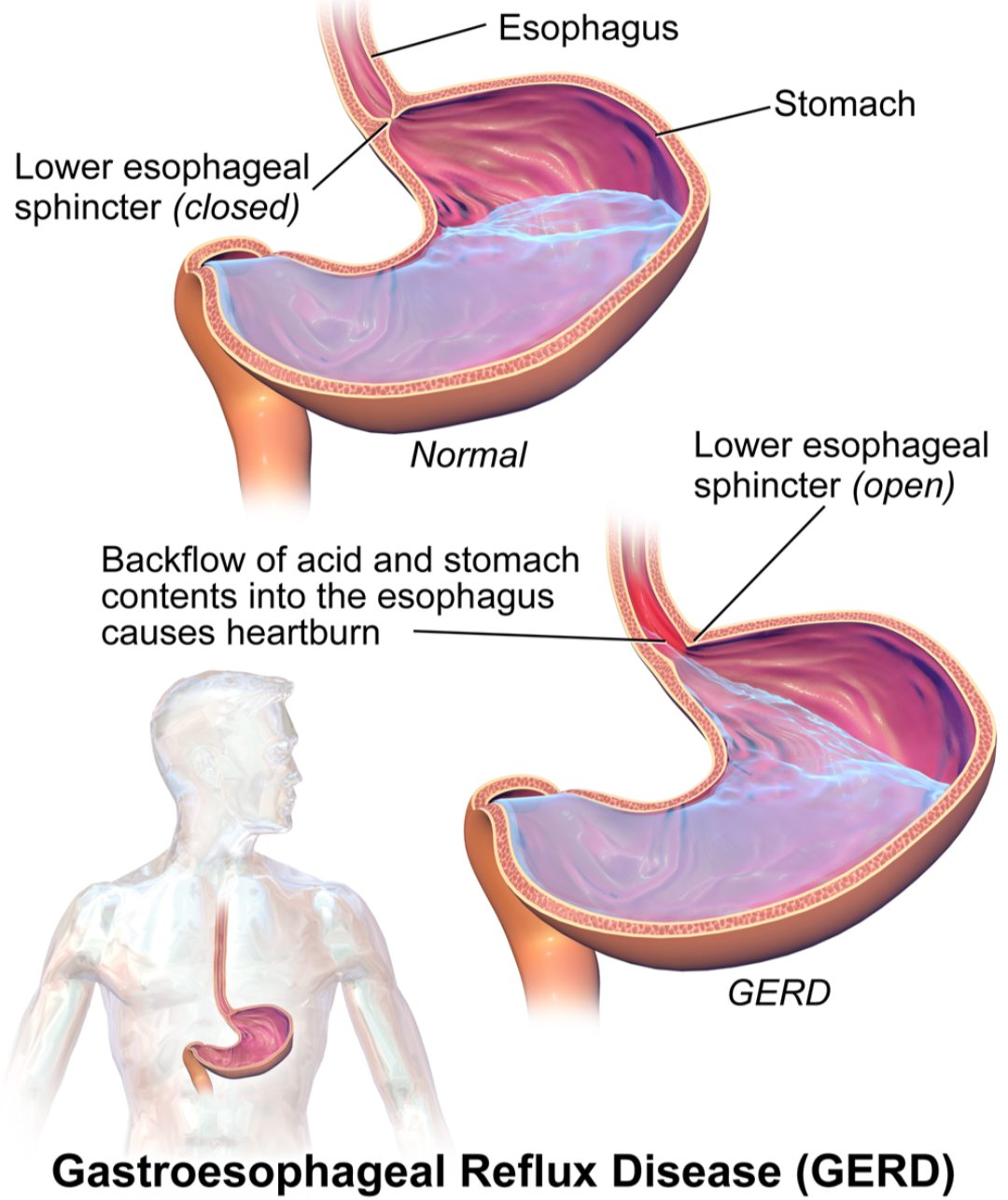
Antacids:
Mode of Action:
Antacids work by neutralizing excess stomach acid, thereby providing rapid relief from symptoms of acidity. They raise the pH of the stomach, reducing the acidity and relieving discomfort.
Common Ingredients:
Aluminum Hydroxide: It reacts with stomach acid to form aluminum chloride and water, reducing acid levels.
Magnesium Hydroxide: It neutralizes acid and can have a laxative effect if used excessively.
Calcium Carbonate: It reacts with stomach acid to form calcium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide, neutralizing acid.
Sodium Bicarbonate: It rapidly neutralizes stomach acid but may lead to increased sodium levels.
Dosage: Antacids are generally taken as needed, 1-2 hours after meals and at bedtime.
Follow package instructions for specific dosages.
Liquid forms should be shaken well before use.
Side Effects: Aluminum-Based Antacids: Can lead to constipation.
Magnesium-Based Antacids: May cause diarrhea.
Calcium Carbonate: Can lead to constipation or, less commonly, an increased risk of kidney stones.
Sodium Bicarbonate: High sodium content may be problematic for individuals with high blood pressure or kidney issues.
Contraindications:
Individuals with kidney problems should avoid magnesium- or aluminum-based antacids.
Those on a low-sodium diet should avoid sodium bicarbonate-based antacids.
H2 Blockers (Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists):
Mode of Action:
H2 blockers reduce stomach acid production by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach lining. This leads to decreased acid secretion, providing relief from acidity symptoms.
Common Medications:
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Cimetidine
Dosage:
Typically taken once or twice a day, as prescribed by a doctor.
Dosage varies based on the specific medication and individual patient needs.
Side Effects:
Common side effects include headache, dizziness, and diarrhea.
Rarely, more severe side effects such as confusion (associated with Cimetidine) may occur.
Long-term use may lead to interactions with other medications.
Contraindications:
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult a doctor before using H2 blockers.
Patients taking other medications should seek medical advice due to potential drug interactions.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
Mode of Action:
PPIs inhibit the enzyme responsible for acid production in the stomach’s parietal cells. This effectively reduces stomach acid levels and provides relief from acidity symptoms.
Common Medications:
Omeprazole
Esomeprazole
Lansoprazole
Dosage:
Taken before a meal, once daily, as prescribed by a doctor.
Dosage may vary depending on the specific PPI and individual patient needs.
Side Effects:
Common side effects include headache, nausea, and stomach pain.
Long-term use may be associated with an increased risk of kidney disease, bone fractures, and reduced magnesium levels.
Contraindications:
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult a doctor before using PPIs.
Patients taking other medications should seek medical advice due to potential drug interactions.
It’s important to note that all medication should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. This information serves as a general guide and should not substitute for personalized medical advice.
Leave a Reply