Detailed information about Acidity Causes and treatment with medicine in detail about antacid medicines their mode of action their daily dosage and side effects and Contraindications
Understanding Acidity: Causes, Treatment, and Antacid Medicines
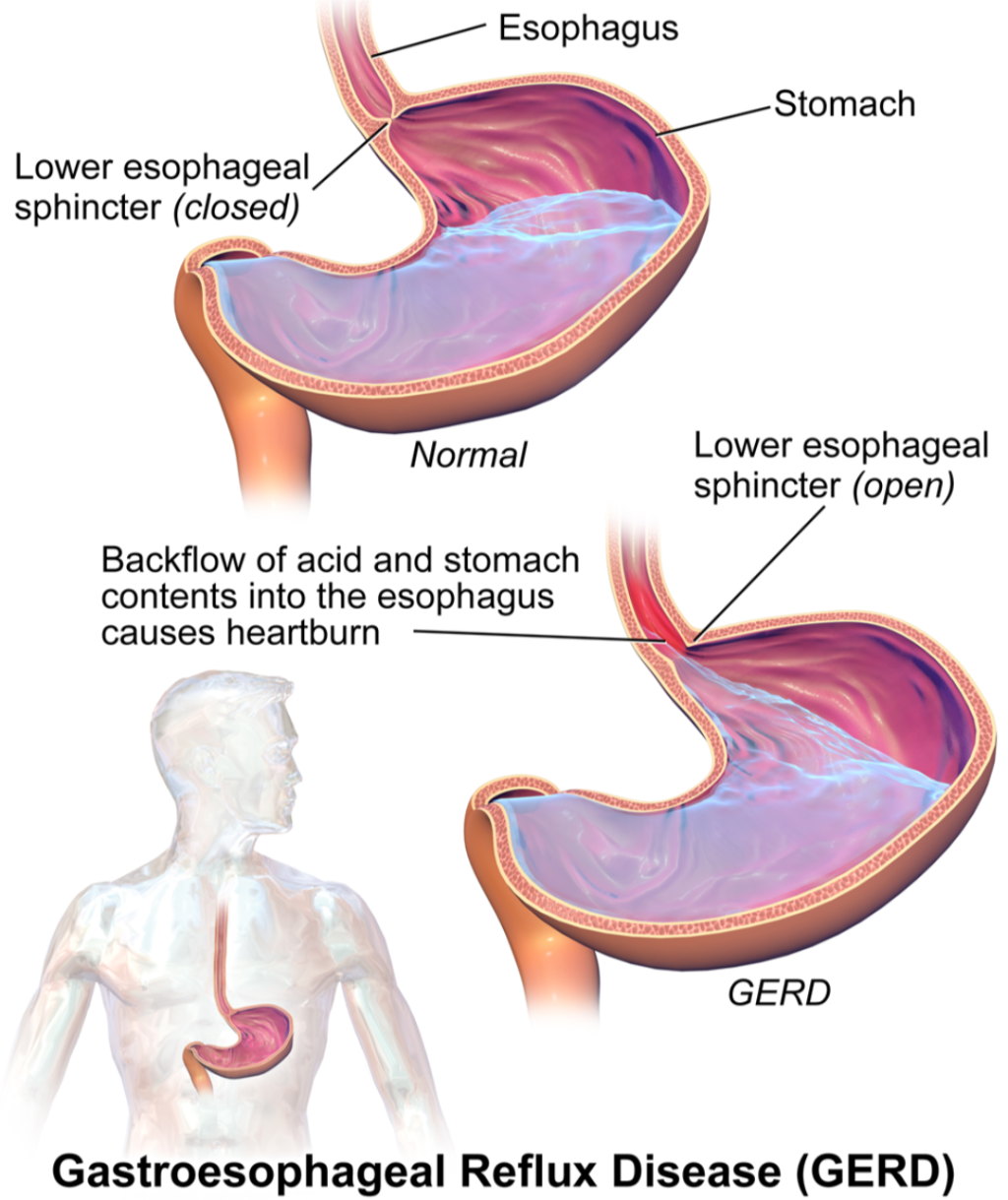
Acidity, commonly known as acid reflux or heartburn, is a digestive disorder characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, leading to discomfort and irritation. This article delves into the causes of acidity, its treatment options, and provides comprehensive information about various antacid medicines, including their modes of action, daily dosages, side effects, and contraindications.
Causes of Acidity:
Dietary Habits: Consuming spicy, fatty, or acidic foods, caffeine, and carbonated beverages can trigger acidity by relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which normally prevents acid reflux.
Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of acidity as they weaken the LES and disrupt the normal digestion process.
Hiatal Hernia: This occurs when a portion of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity, putting pressure on the LES and causing acid reflux.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach during pregnancy can lead to acid reflux.
Certain Medications: Some medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain blood pressure medications, can contribute to acidity.
Antacid Medicines and Treatment:
Antacids:
Mode of Action: Antacids neutralize stomach acid, providing quick relief from acidity symptoms by raising the pH of the stomach.
Common Ingredients: Aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate.
Daily Dosage: Generally taken as needed, 1-2 hours after meals and at bedtime. Follow package instructions.
Side Effects: Constipation (with aluminum-based antacids) or diarrhea (with magnesium-based antacids).
Contraindications: Individuals with kidney problems, high blood pressure, or those on a low-sodium diet should consult a doctor before using sodium bicarbonate-based antacids.
H2 Blockers (Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists):
Mode of Action: H2 blockers reduce stomach acid production by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach lining.
Common Medications: Ranitidine, Famotidine, Cimetidine.
Daily Dosage: Typically taken once or twice a day, as prescribed by a doctor.
Side Effects: Headache, dizziness, and rarely, more severe side effects like confusion (Cimetidine).
Contraindications: Consult a doctor before use if pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
Mode of Action: Proton pump inhibitors PPIs inhibit acid production by blocking the enzyme responsible for producing stomach acid.
Common Medications: Omeprazole, Esomeprazole, Lansoprazole.
Daily Dosage: Taken before a meal, once daily, as prescribed by a doctor.
Side Effects: Potential long-term use risks include kidney disease, bone fractures, and reduced magnesium levels.
Contraindications: Consult a doctor if pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications.
Acidity is a common digestive issue that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. By understanding the causes of acidity and the various treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms effectively. Antacid medicines, including antacids, H2 blockers, and PPIs, offer different mechanisms of relief and should be chosen based on individual needs and medical advice. As with any medication, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment regimen to ensure the most suitable and safe approach to managing acidity.
Leave a Reply